UX (user experience) design and UI (user interface) design are two closely related but distinct fields essential to creating effective and user-friendly digital products.
What is UX Design?
UX (user experience) design is designing digital products, computerised devices, or services that provide a positive and meaningful experience for users. It involves understanding the needs and behaviours of users and using that knowledge to create graphical user interfaces and interactions that are intuitive, easy to use, and effective.
The main goal of UX design is to create a product that meets the needs and expectations of the target audience and is enjoyable and satisfying to use. This requires a deep understanding of the user and the ability to anticipate their needs and behaviours throughout the design process.
UX design typically involves several stages, including user research, persona development, user flows, wireframing, prototyping, and user testing. Each stage is focused on gathering user insights and feedback and using that information to inform design decisions.
The ultimate output of UX design is a set of design recommendations that inform the overall structure and functionality of the digital product or service. These recommendations may include detailed graphical user interfaces, flows, wireframes, and prototypes that help developers and stakeholders understand the design vision.
Overall, UX design is critical to creating successful digital products and services. It helps ensure that the user’s needs and expectations are at the forefront of the design process.
What is UI Design?
UI (user interface) design is designing the visual and interactive aspects of a digital product or service, such as a best user experience websites or mobile app. It involves creating a visually appealing and intuitive interface that allows users to interact with the product seamlessly and effectively.
The main goal of UI design is to create an aesthetically pleasing interface that is easy to use and provides users with clear and intuitive feedback. This requires a deep understanding of the user’s needs and behaviours, an eye for design, and attention to detail.
UI design typically involves creating visual mockups and prototypes that demonstrate the interface’s layout, typography, colour scheme, and other design elements. Designers work to create a consistent visual style that reflects the brand identity and meets the target audience’s needs.
UI designers also work closely with developers to ensure the interface is implemented correctly and functions as intended. They provide detailed design specifications and assets, such as icons, buttons, and other UI elements, that developers can use to build the product.
Overall, UI design is essential to creating successful digital products and services, as it helps ensure that the user can interact with the product seamlessly and intuitively.
Differences Between UX and UI Design
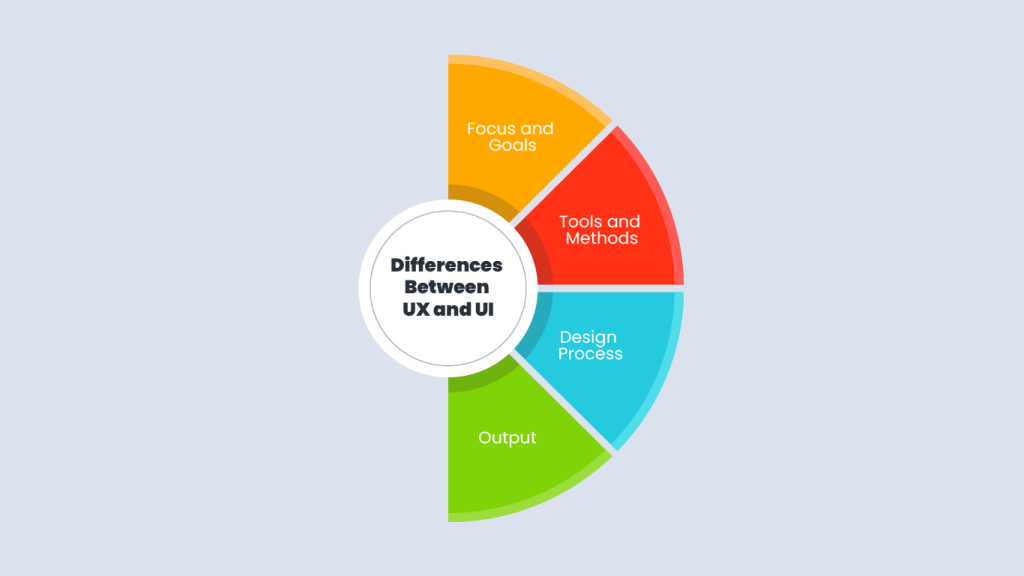
While UX (user experience) design and UI (user interface) design share some similarities, they are two distinct and complementary fields that focus on different aspects of the design process. Here are some key differences between UX and UI design:
1. Focus and Goals:
The main focus of UX design is to create a product that meets the needs and expectations of the user, with the goal of creating a positive and meaningful customer experience. UX designers work to ensure that the product is easy to use, effective, and enjoyable to interact with.
The main focus of Good UI design is to create a visually appealing and intuitive interface that allows users to interact with the product seamlessly and effectively. UI designers work to create a consistent visual style that reflects the brand identity and meets the needs of the target audience.
2. Tools and Methods:
UX designers use various tools and methods to research and understand the needs and behaviours of users. They may conduct surveys, interviews, and usability tests and use data analysis to inform their design decisions. They also use wireframes and prototypes to communicate the structure and functionality of the product.
UI designers use design software tools to create visual mockups and prototypes of the interface. They use typography, colour, and visual hierarchy to create an aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly interface. They also provide detailed design specifications and assets for developers to use when building the product.
3. Design Process:
The design process for UX design involves conducting user research, creating personas, mapping out user journeys, and developing wireframes and prototypes to test and refine the product’s overall structure and functionality.
The design process for UI design involves creating visual mockups and prototypes that demonstrate the interface’s layout, typography, colour scheme, and other design elements. Designers work to create a consistent visual style that reflects the brand identity and meets the target audience’s needs.
4. Output:
The output of UX design is a set of user-centred design recommendations, wireframes, and user flows that inform the overall structure and functionality of the digital product.
The output of UI design is a visual design that reflects the brand identity and is aesthetically pleasing and easy to use. It includes detailed design specifications and assets for developers to use when building the product.
Overall, while UX and UI design share some similarities, they are two distinct and complementary fields focusing on different aspects of the design process. While UX design is focused on creating a positive abbreviation for user experience, UI design is focused on creating a visually appealing and intuitive interface.
Understanding the Roles of UX Designers and UI Designers
UX (user experience) designers and UI (user interface) designers are two distinct roles that work together to create compelling digital products. Here is an overview of the responsibilities and skills of each role:
1. UX Designer:
The role of a UX designer is to create a positive and meaningful user interface experience. Their primary responsibilities include:
- Conducting user research to understand the needs and behaviours of users
- Creating user personas to represent the target audience
- Mapping out user journeys to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement
- Developing wireframes and prototypes to test and refine the product’s overall structure and functionality
- Conducting usability tests to ensure that the product is easy to use and meets the needs of the user
- We are collaborating with other design and development team members to ensure that the product is delivered on time and meets the needs of the business and the user.
The skills required for a UX designer include the following:
- Knowledge of user-centred design principles and methodologies
- Vital research and analysis skills
- Proficiency in design tools such as Sketch, Figma, or Adobe XD
- Ability to create wireframes and prototypes
- Understanding of front-end development and coding languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
- Strong communication and collaboration skills.
2.UI Designer:
The role of a UI designer is to create a visually appealing and intuitive interface. Their primary responsibilities include:
- Creating visual mockups and prototypes that demonstrate the layout, typography, colour scheme, and other design elements of the interface
- Ensuring that the interface is consistent with the brand identity and meets the needs of the target audience
- Providing detailed design specifications and assets for developers to use when building the product
- We are collaborating with other design and development team members to ensure that the product is delivered on time and meets the needs of the business and the user.
The skills required for a UI designer include the following:
- Knowledge of design principles and best practices
- Strong visual design skills, including typography, colour theory, and layout
- Proficiency in design tools such as Sketch, Figma, or Adobe XD
- Ability to create high-fidelity visual designs and prototypes
- Understanding of front-end development and coding languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
- Strong communication and collaboration skills.
Overall, while UX and UI designers have different roles and responsibilities, they work closely together to create compelling digital products that meet the needs of the user and the business.
What Does a UX Designer Do?
A UX (user experience) designer is responsible for creating a positive and meaningful experience for digital products or service users. Here are some of the critical tasks and responsibilities of the job titles a UX designer:
1. User Research:
One of the primary responsibilities of a UX designer is to conduct user research to understand the needs and behaviours of users. This may involve conducting surveys, user interviews, and usability tests to help the best app interface user experience designer gather feedback and insights about human users of the product.
2. Creating User Personas:
Based on the user research, a UX front interaction designer then creates user personas and mental models that represent the product’s target audience. These personas help the front interaction designer to better understand the user’s goals, needs, and behaviours.
3. Information Architecture:
A UX designer works on the information architecture of a product, which involves organizing the content and functionality of the product in a way that is easy to understand and use.
4. Creating Wireframes and Prototypes:
A UX designer creates wireframes and prototypes to test and refine the product’s structure and functionality. This may involve creating low-fidelity sketches, mockups, more detailed wireframes, and interactive prototypes.
5. Conducting Usability Testing:
A UX designer conducts usability tests to ensure that the product is easy to use and meets the user’s needs. This involves conducting user testing, observing users as they interact with the product and gathering feedback to identify areas for improvement.
6. Collaborating with Other Designers and Developers:
A UX designer collaborates with other design and development team members to ensure that the product is delivered on time and meets the needs of the business and the person’s experience as the user.
Overall, the goal of a UX designer is to create a positive and meaningful user experience that meets the needs and expectations of the user. This requires a combination of research, design, and collaboration skills, a design thinking process, and a deep understanding of user-centred design principles and methodologies.
What Does a UI Designer Do?
A UI (user interface) designer is responsible for designing the visual aspects of a digital product or service. Here are some of the critical tasks and responsibilities of a UI designer:
1. Creating Visual Designs:
A UI designer creates visual designs for digital products, including the layout, typography, colour scheme, and other design elements of the interface. They ensure that the visual design is consistent with the brand identity and meets the target audience’s needs.
2. Providing Design Specifications:
A UI designer provides detailed design specifications and assets for developers to use when building the product. This service designer job search includes creating style guides, design libraries, and other resources that help ensure consistency and efficiency throughout the development process.
3. Creating High-Fidelity Visual Designs:
A UI designer creates high-fidelity visual designs and prototypes that demonstrate the final look and feel of the product. This may involve creating detailed mockups and interactive augmented reality prototypes that showcase the product’s functionality and visual design.
4. Collaborating with Other Designers and Developers:
A UI designer collaborates with other design and development team members to ensure that the product is delivered on time and meets the needs of the business and the user. This may involve working closely with UX designers, developers, and project managers to ensure the visual design aligns with the overall product vision and goals.
Overall, the goal of a UI designer is to create a visually appealing and best ui interface design that meets the needs and expectations of the user. This requires a combination of visual design skills, attention to detail, critical thinking, collaboration skills, and a deep understanding of design principles and best practices.
How UX and UI Design Work Together
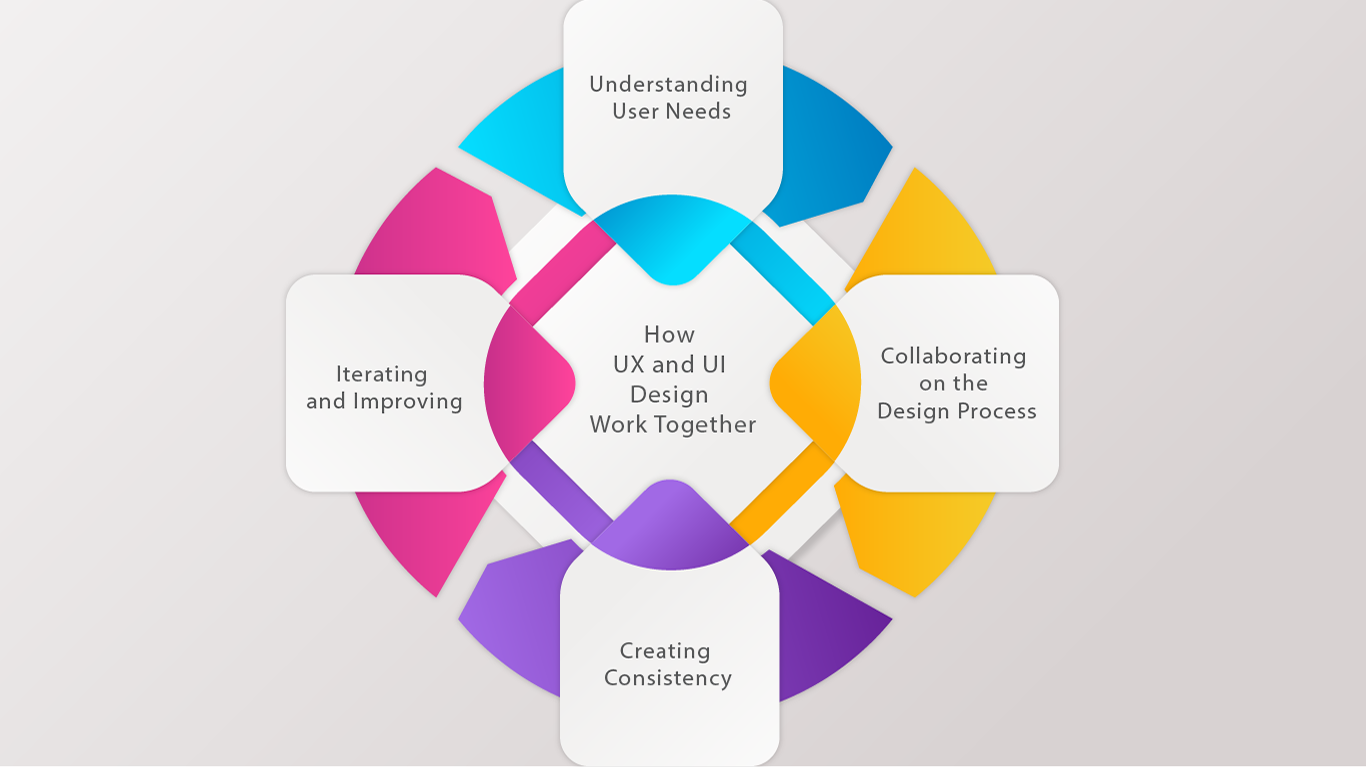
UX (user experience) and UI (user interface) design are closely related and often work together to create a cohesive digital product or service. Here are some ways in which UX and UI design work together:
1. Understanding User Needs:
Both UX and UI designers need to understand the needs and behaviours of users to create an effective product. UX designers conduct user research to understand the user’s goals, needs, and behaviours. In contrast, UI+ designers aim to use this information to create a visually appealing and intuitive interface that meets those needs.
2. Collaborating on the Design Process:
UX and UI designers often work together closely throughout the design process. UX designers create wireframes and prototypes to test and refine the overall structure and functionality of the product, while UI designers use these prototypes to create high-fidelity visual designs that reflect the final look and feel of the product.
3. Creating Consistency:
Consistency is essential in creating a positive user experience. UX and UI designers work together to ensure the product’s visual design is consistent with the overall user experience and brand identity. They also create design libraries and style guides that provide developers with a clear set of design specifications to ensure consistency throughout the product.
4. Iterating and Improving:
UX and UI designers work together to iterate and improve the product based on user feedback and testing. UX designers use this feedback to refine the overall structure and functionality of the product. In contrast, UI designers use it to adjust the visual design and user-interface elements.
Overall, UX and UI design work together to create a positive and meaningful user experience that meets the needs and expectations of the user. This requires an interaction design foundation, a severe interaction design foundation and close collaboration between the two disciplines throughout the design process to ensure a cohesive and effective product.
How to Make a Great UX Design and Smooth UI Design
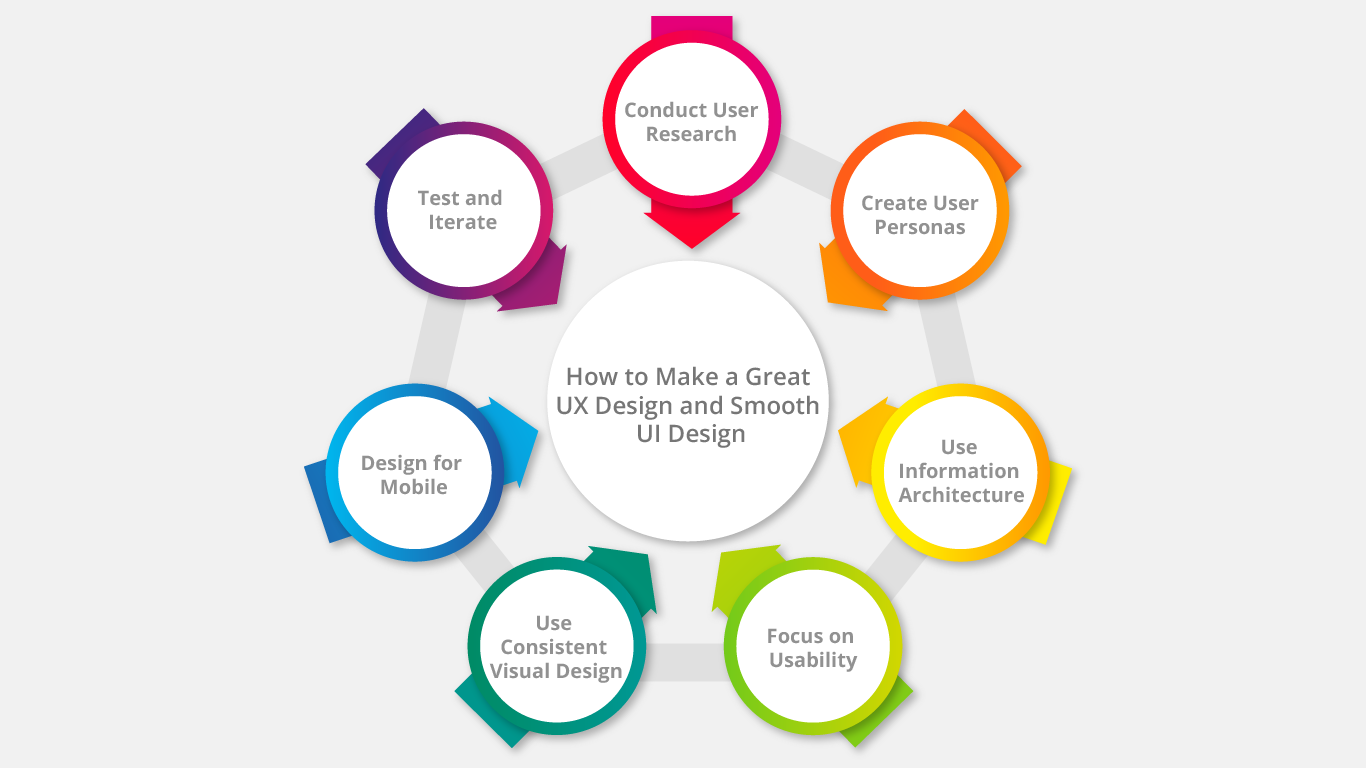
Creating a great UX (user experience) design and smooth UI or good usability (user interface) design requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a deep understanding of the needs and behaviours of the target audience. Here are some tips for making a great UX design and smooth UI or ux design or good usability design:
1. Conduct User Research:
UX and interaction designers should conduct user research to understand the needs and behaviours of the target audience. This can involve surveys, interviews, and other forms of user testing to have interaction designers gain insights into user preferences and pain points.
2. Create User Personas:
Creating user personas can help UX designers create a product that meets the needs and preferences of the target audience. User personas are fictional representations of the target audience based on user research and other data and can be used to inform design decisions throughout the design process.
3. Use Information Architecture:
In information architecture, content is organised and structured to make it easy for users to find and use. UX designers should use information architecture principles to create a clear, intuitive navigation structure that guides users through the product.
4. Focus on Usability:
Usability is a critical component of a great UX design. UX designers should focus on creating a product that is easy to use, with intuitive and straightforward workflows that help users accomplish their goals quickly and efficiently.
5. Use Consistent Visual Design:
Consistent visual design is an essential component of a smooth UI design. UI designers should use a consistent graphic design, language and visual style throughout the product to create a cohesive and polished user interface.
6. Design for Mobile:
Mobile design is becoming increasingly important as users access digital products and services on mobile devices. UX and UI designers should design for mobile devices, focusing on creating a responsive and mobile-friendly interface optimised for touch interactions.
7. Test and Iterate:
UX and UI design are iterative processes that require constant usability testing and refinement. Designers should test the product with real users, gather feedback, and use this feedback to improve the design.
By following these essential UI/UX tips, designers can create a great user experience and a smooth user interface that meets the needs and preferences of loyal customers and the target audience.
What Skills Are Required for a UX/UI Designer?
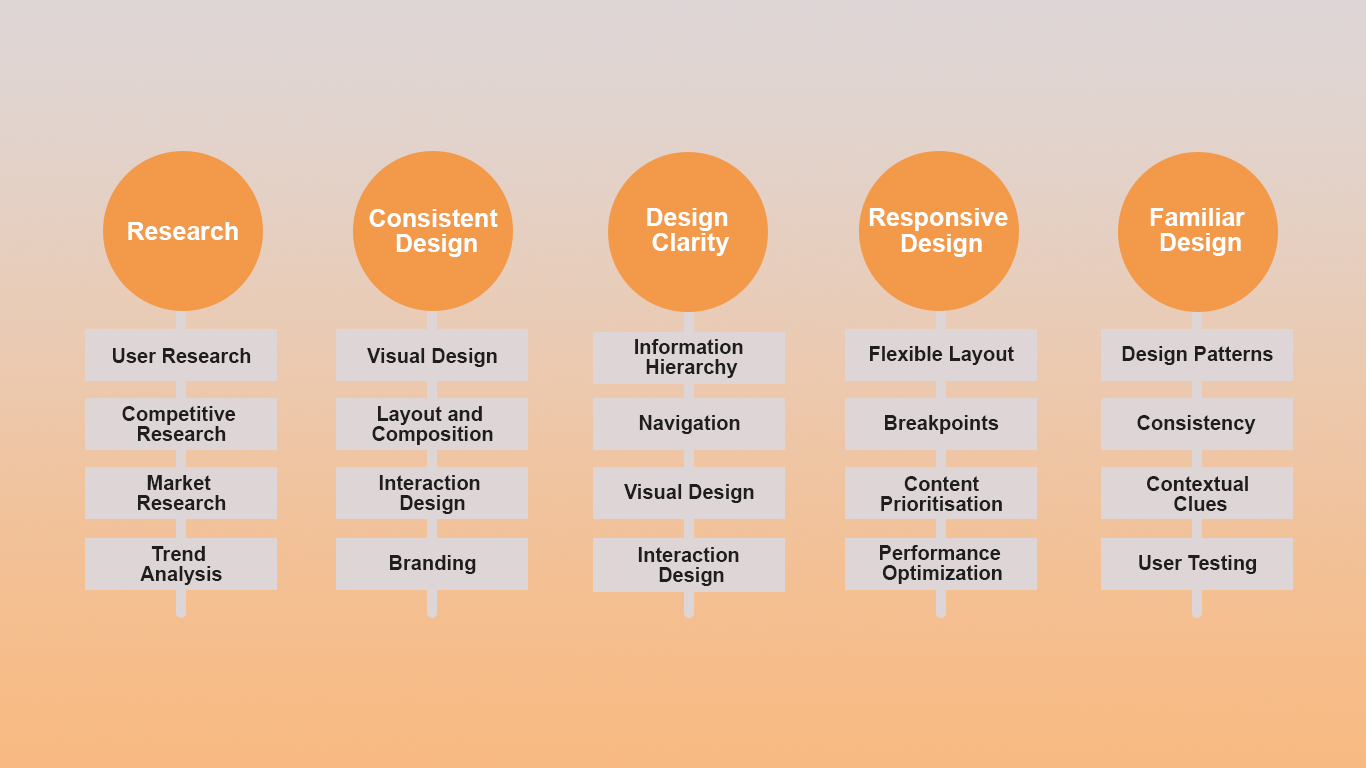
Research
Research is a critical component of UX (user experience) and UI (user interface) design, as it provides designers with insights into the needs and behaviours of users and the broader market landscape. Here are some key types of research that UX and UI designers may conduct:
1. User Research:
User research involves gathering data and insights about the target audience’s needs, preferences, and behaviours. This can involve surveys, interviews, focus groups, and usability testing, among other methods. User research can help designers understand how users interact with digital products and services and identify pain points and areas for improvement.
2. Competitive Research:
Competitive research involves analysing the digital products and services of competitors in the market. This can provide designers with insights into emerging trends and best practices, a competitive advantage, and opportunities to differentiate the product or service from competitors.
3. Market Research:
Market research involves gathering data and insights about the broader market landscape, including industry trends, consumer preferences, and market opportunities. Market research can help designers understand the competitive landscape, identify areas of growth and opportunity, and make strategic decisions about the product or service.
4. Trend Analysis:
Trend analysis involves analysing emerging UX and UI design trends and broader cultural and technological trends. This can provide designers with insights into emerging design patterns, user expectations, and technological advancements, which can inform the design of the product or service.
Overall, research is a critical component of UX and UI design, as it helps designers create digital products and services that meet the needs and preferences of the target audience while also considering broader market and cultural trends. By conducting research throughout the design process, designers can create products and services that are both effective and relevant in today’s digital landscape.
Consistent Design
Consistent design is a crucial principle of UI (user interface) design. It refers to maintaining a consistent visual language and design style throughout a digital product or service. Here are some critical aspects of consistent design:
1. Visual Design:
The visual design uses colours, typography, and other elements to create a cohesive and polished design language. Consistent visual design involves using the same design elements and language throughout the product to create a seamless and intuitive user experience.
2. Layout and Composition:
Layout and composition refer to the arrangement of visual elements within the user interface. Consistent layout and composition involve using the same design patterns and layouts throughout the product to create a sense of familiarity and predictability for the user.
3. Interaction Design:
Interaction design refers to the design of the interactions between the end user interaction and the product. Consistent interaction design involves using the same design patterns and interactions throughout the product to create a sense of familiarity and ease of use for the end user.
4. Branding:
Branding refers to using visual and verbal elements to communicate the identity and personality of a brand. Consistent branding involves using the same visual and verbal elements throughout the product to create a cohesive and recognizable brand identity.
Overall, consistent design is essential because it helps create a seamless and intuitive user experience while communicating a solid and cohesive brand identity to loyal customers. By using consistent design language and style throughout the product, designers can create a sense of familiarity and ease of use, ultimately leading to a more positive and practical user experience.
Design Clarity
Design clarity refers to the degree to which a design is straightforward to understand for the user. In UI (user interface) design, clarity is essential because it helps users navigate and interact with digital products and services more quickly and efficiently. Here are some critical aspects of design clarity:
1. Information Hierarchy:
Information hierarchy refers to the organisation and prioritisation of information within the user interface. Clear information hierarchy involves using typography, colour, and other design elements to indicate the Importance of UI/UX Design and relationship between different pieces of information. This helps users quickly and easily understand the purpose and function of different elements within the interface.
2. Navigation:
Navigation refers to how users move through the interface. Straightforward navigation involves using consistent and intuitive design patterns to help users understand how to navigate through the product or service. This can include clear labelling, consistent placement of navigation elements, and a logical and predictable user flow through the interface.
3. Visual Design:
The visual design uses colours, typography, and other elements to create a cohesive and polished design language. Straightforward visual design involves using design elements that are easy to read and understand and communicate information clearly and effectively.
4. Interaction Design:
Interaction design refers to the interactions between the user and the product. Straightforward interaction design involves using intuitive and consistent design patterns to help users understand how to interact with the product or service and provide clear and easy-to-understand feedback.
Overall, design clarity is essential for creating effective and efficient user experiences. By using clear and consistent design patterns, designers can help users understand the purpose and function of different elements within the interface and navigate through the product or service with ease. This can lead to a more positive and practical user experience and help to achieve the goals of the product or service.
Responsive Design
Responsive design is a design approach that enables a digital product or service to adapt to different screen sizes and devices. This means the design should adjust and optimise its layout, content, and functionality to provide a consistent and seamless user experience across different devices, from desktop computers to mobile phones and tablets. Here are some key aspects of responsive design:
1. Flexible Layout:
Responsive graphic design requires a flexible layout that can adapt to different screen sizes and resolutions. This involves using fluid grid systems and scalable images that adjust proportionally to the available screen space.
2. Breakpoints:
Breakpoints are specific screen sizes the design should adjust to provide the best user experience. For the best ui examples, a design may have a breakpoint where the layout shifts from a three-column layout to a two-column layout on smaller screens.
3. Content Prioritisation:
Content prioritisation involves identifying which content and features are most important to the user’s experience and ensuring they are presented prominently and easily accessible across different devices. This may involve hiding or collapsing some aspects on smaller screens or reordering content to fit smaller screen sizes.
4. Performance Optimization:
Responsive design also requires optimising the product or service’s performance across different devices. This may involve optimising images, reducing file sizes, and minimising code to ensure the product loads quickly and efficiently on different devices.
Responsive design is essential for creating a seamless and consistent user experience across different devices. By designing for flexibility and prioritising content and functionality, designers can ensure that their products and services are accessible and effective for users across various devices and screen sizes.
Familiar Design
Familiar design refers to using design patterns and conventions that users are already familiar with from previous experiences with similar products or services. The familiar design aims to provide a more intuitive and user-friendly experience by reducing cognitive load and making it easier for users to understand how to interact with a new product or service.
Here are some critical aspects of familiar design:
1. Design Patterns:
There are established solutions to common design problems called design patterns. The familiar design uses well-known design patterns that users already know, such as navigation menus, search bars, and forms. By using these established patterns, designers can help users navigate and interact more efficiently with the product or service.
2. Consistency:
Consistency is vital to a familiar design. Designers should use consistent design patterns, visual language, and interactions throughout the product or service to provide users with a cohesive and familiar experience. This can help users feel more comfortable and confident when using a new product or service.
3. Contextual Clues:
Contextual clues are visual cues, accessible design, and physical interaction that provide users with information about the purpose and function of different elements within the interface. The familiar design uses contextual clues that users are already familiar with, such as button styles and colour schemes. This can help users quickly understand how to interact with different elements within the interface.
4. User Testing:
User testing is an essential aspect of the familiar design. By usability testing different design patterns and interactions with real users, designers can identify which patterns and conventions are most familiar and intuitive for their target audience. This can also help designers create a more familiar and user-friendly experience for their target users.
Overall, familiar design is essential for creating a user-friendly and intuitive user experience. By using established design patterns and conventions, designers can reduce cognitive load and make it easier for users to understand how to interact with a new product or service. Consistency and contextual clues also play a crucial role in creating a cohesive and familiar user experience.
Final Thoughts on UX and UI Design
UX and UI design are critical to creating successful digital products and services. By understanding user needs and behaviours, UX design creates a seamless and intuitive user interface experience. In contrast, UI design focuses on the visual and interactive elements users interact with on the screen.
While there are distinct difference between UX and UI design, the two disciplines work together to create a cohesive and effective user experience. By collaborating and communicating effectively, Hire UX and UI designers, They can ensure that the design of a product or service meets both the functional and aesthetic needs of its users.
Successful UX and UI design principles include conducting user research, creating full user stories and personas, designing for consistency, prioritising content, and incorporating familiar design patterns. Additionally, designing with responsiveness in mind is crucial in today’s digital landscape, where users access products and services from various devices.
Overall, UX and UI design are essential components of creating successful digital products and services that meet the needs and expectations of their users. By putting users at the center of the digital design and process and following best practices in UX and UI design, designers can create products and services that are both effective and enjoyable to use.
What good is an idea if it remains an idea? Let's put efforts together to give it a look of Website or Mobile Application.
Let’s Start a discussion



